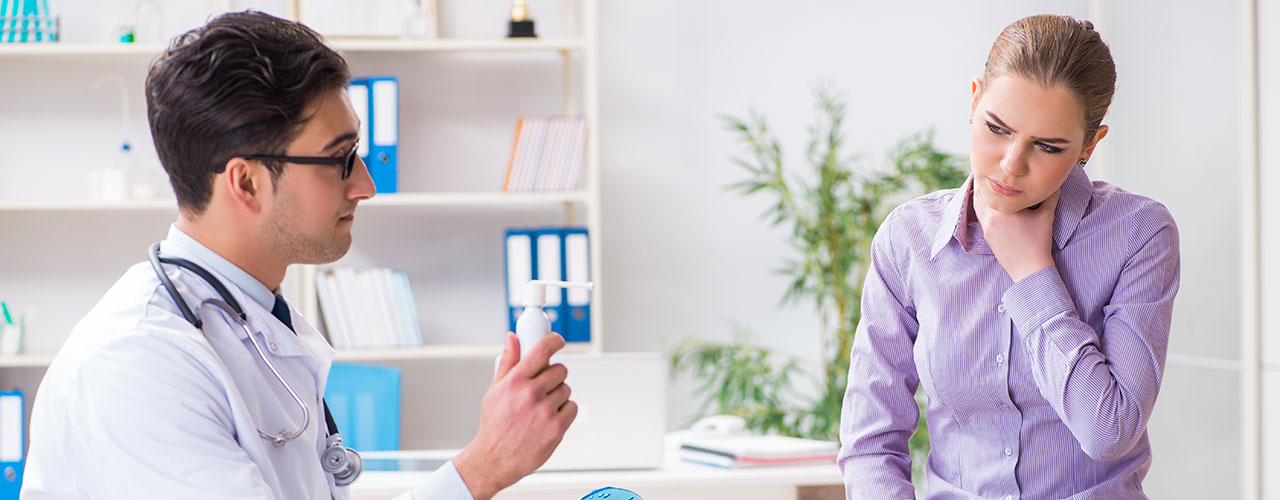
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the vocal cords that results in changes in a person's voice.
Laryngitis can be grouped into two categories: acute and chronic. The causes and treatments for each type vary.
- Acute laryngitis is a temporary condition that is often caused by an infection or simple overuse of the vocal cords.
- Chronic laryngitis may also be caused by frequent overuse of the vocal cords, personal habits, or by a more serious underlying condition.
Causes of Laryngitis
Acute laryngitis is typically associated with relatively benign causes. Infection with a cold or other short-term condition affecting the throat may be the cause. Often, the cause of acute laryngitis is that a patient has simply put too much strain on their vocal cords. Shouting, loud singing, or a prolonged speech can overwork the larynx, causing inflammation.
Chronic laryngitis—laryngitis lasting longer than two weeks—can also be caused by overuse. This is often seen in those who use their voice every day as part of a profession. However, chronic laryngitis can also indicate a more serious health condition that needs to be addressed.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption may contribute to chronic laryngitis. Exposure to debris or chemical irritants is another potential cause. Environmental causes such as these should be addressed for relief of laryngitis symptoms, but also because they may lead to more serious complications in the future. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, can also cause chronic laryngitis. Stomach acid frequently backs up into the esophagus in GERD sufferers. Over time, this may irritate the vocal cords. Less common causes of laryngitis may include chronic postnasal drip, cancer, or paralysis of the vocal cords.


Symptoms of Laryngitis
The most common symptom of laryngitis is a vocal abnormality, such as a weak voice or loss of voice. Patients may experience “cracking” in their speech or find that their voice has a low, raspy tone that is out of character with their normal voice. Other symptoms might include throat discomfort, difficulty when swallowing, a tickling sensation, or a dry cough. Any combination of these symptoms may be present.
Treatment of Laryngitis
A doctor will typically diagnose laryngitis with a physical exam that involves listening to the patient’s voice and examining the throat. Sometimes a biopsy may be performed to rule out the most serious causes. It is possible for a case of acute laryngitis to require no medical treatment at all. Sometimes, the condition will improve on its own with self-care at home. If there is an infection, an antibiotic may be prescribed.
When laryngitis is chronic, treatment will vary widely depending on the cause. Resting the voice for a time may be recommended if the cause is frequent overuse. Patients may need to quit smoking or drinking. Adjustments at work or time off may be required in cases of exposure to hazards. Underlying conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease, chronic sinus conditions, tumors, or cancers will need to be treated if they are present.


